Your employees can play a pivotal role in safeguarding your organization’s digital assets and information. Let us take a deeper dive into the essential cybersecurity best practices for your employees, including maintaining strong passwords, being vigilant about phishing attempts, regularly updating software, securing physical devices, and fostering a culture of security awareness.
Cybersecurity Best Practices for Employees
#1: Maintaining Strong Passwords
One of the simplest yet most effective cybersecurity measures is the use of strong, unique passwords. Strong passwords are essential because they:
- Prevent unauthorized access: Complex passwords are harder for attackers to guess or crack using brute-force methods.
- Protect personal and organizational data: Secure passwords safeguard sensitive information from being compromised.
- Comply with security standards: Many regulatory frameworks require the use of strong passwords as part of their compliance requirements.
Characteristics of Strong Passwords
You should encourage your employees to create passwords that are difficult to guess, which include a mix of letters, numbers, and special characters. A strong password should have the following characteristics:
- Length: The longer a password, the more secure it is. A minimum of 12 characters is recommended, but 16 or more is preferable.
- Complexity: It should include a mix of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters to increase its complexity.
- Unpredictability: Avoid predictable patterns, such as “123456,” “password,” or keyboard patterns like “qwerty.”
- Uniqueness: Each account or service should have a unique password. Reusing passwords across multiple sites increases the risk if one site is compromised.

Best Practices for Creating & Managing Strong Passwords
- Use a passphrase: Consider using a phrase or a combination of words that are easy for you to remember but hard for others to guess. Incorporating randomness and complexity within the passphrase enhances its strength.
- Employ password managers: Password managers generate strong, unique passwords for each of your accounts and securely store them, so you do not have to remember every single one. They can also help you change passwords regularly.
- Leverage multi-factor authentication (MFA): Even the strongest passwords can be compromised. Enabling MFA, where available, adds an extra layer of security by requiring additional verification (such as a code sent to your phone) to gain access.
- Educate about social engineering: Be aware of social engineering tactics used to trick individuals into revealing their passwords. Never share your passwords and be cautious of phishing attempts.
Regularly Update and Review Passwords
- Change passwords regularly: Regularly updating your passwords can help protect against ongoing threats, especially after a breach.
- Audit password practices: Regularly review your password practices and the security of the services you use. This includes checking for breaches that may affect your accounts and updating passwords accordingly.
#2: Vigilance Against Phishing Attempts
A recent study revealed that 88% of data breach incidents were caused by employee error. Therefore, being vigilant against phishing attempts is crucial as these types of cyberattacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated and prevalent.
Phishing is a method used by cybercriminals to deceive individuals into providing sensitive information, such as usernames, passwords, credit card details, or other personally identifiable information. This is often achieved using fraudulent emails, messages, websites, or phone calls that mimic legitimate organizations or individuals.
Understanding how to recognize and respond to phishing attempts is essential for protecting your organization from potential harm.
Recognizing Phishing Attempts
Phishing attempts can be recognized by several key indicators:
- Suspicious Email Addresses: The sender’s email might closely mimic a legitimate address but include slight misspellings or use a misleading domain.
- Urgent or Threatening Language: Messages may create a sense of urgency or fear, prompting immediate action, such as verifying your account details or making a payment to avoid negative consequences.
- Unsolicited Attachments or Links: Phishing emails often contain attachments or links that the recipient is urged to open or click. These can lead to malicious websites or download malware onto the user’s device.
- Requests for Personal Information: Legitimate organizations typically do not ask for sensitive information through email or text messages. Be wary of any unsolicited requests for your personal or financial details.
- Generic Greetings: Phishing attempts may use generic greetings like “Dear Customer” instead of your name, indicating a lack of personalization typical in legitimate communications.
Best Practices for Vigilance
To protect against phishing attempts, you should adopt the following best practices for your employees:
- Verify the Source: Before responding to any requests for information or clicking on links, verify the legitimacy of the source. This can be done by contacting the organization directly using contact information obtained from their official website or other trusted sources.
- Use Spam Filters: Email services often include spam filters that can help detect and isolate phishing emails. Make sure these filters are activated and correctly configured to maximize their effectiveness.
- Educate and Train: Regular training and awareness programs can help individuals recognize phishing attempts and understand the protocols for reporting and handling these incidents.
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an additional layer of security, making it more difficult for attackers to gain access to your accounts, even if they manage to obtain your credentials.
- Keep Software Updated: Ensure that all software, especially antivirus and antimalware programs, are up to date. These tools can help detect and prevent phishing attempts and other cyber threats.
Reporting Phishing Attempts
If your employee suspects they have received a phishing attempt, they should report the attempt immediately.
- Within Your Organization: Notify your IT or cybersecurity team immediately. They can take steps to prevent further attempts and mitigate any potential damage.
- To Relevant Authorities: In many countries, you can report phishing emails to government or cybersecurity organizations. Reporting can help these entities track phishing campaigns and potentially take action against the perpetrators.
Educating your employees on the importance of verifying the authenticity of emails and not clicking on links or downloading attachments from unknown sources is crucial in mitigating the risk of phishing attacks.
#3: Regular Software Updates
Keeping software up to date is another critical cybersecurity best practice for employees when protecting your organization against cyber threats. Cybercriminals often exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software to gain unauthorized access to systems and data.
Your employees should ensure that their operating systems, applications, and antivirus software are regularly updated to the latest versions. Automating software updates can help in ensuring that software is always up to date without relying on manual intervention.

The Importance of Regular Software Updates
- Patch Security Vulnerabilities: Software updates often include patches for security vulnerabilities that have been discovered since the last update. By exploiting these vulnerabilities, attackers can gain unauthorized access to systems, steal data, or cause other types of harm.
- Enhance System Stability: Updates can fix bugs and other issues that affect the stability and performance of software. This ensures that systems run smoothly and are less likely to experience crashes or other problems that could be exploited by attackers.
- Introduce New Security Features: Developers frequently include new security features in updates to provide better protection against threats. Failing to update means missing out on these enhancements.
- Comply with Regulations: Certain industries are subject to regulations that require maintaining up-to-date software to protect sensitive information. Regular updates help ensure compliance with these legal requirements.
Best Practices for Implementing Regular Software Updates
- Enable Automatic Updates: Wherever possible, enable automatic updates for operating systems, applications, and security software. This ensures that the software is updated as soon as new versions are released without requiring manual intervention.
- Prioritize Critical Updates: Sometimes, updates are categorized by their importance, with some addressing critical security vulnerabilities. It is important to prioritize these updates and apply them immediately.
- Maintain an Update Schedule: For software that cannot be updated automatically, maintain a regular schedule for checking and applying updates. This can be weekly, bi-weekly, or monthly, depending on the software and the level of risk associated with it.
- Educate and Train Employees: Ensure that your employees understand the importance of software updates and know how to apply them. This is particularly important for remote workers who may be using personal devices for work.
- Use Patch Management Tools: If your organization has several devices and applications, it can benefit from patch management tools. These tools help automate the process of tracking, downloading, and applying software updates across multiple devices.
#4: Securing Physical Devices
In addition to digital security measures, physical security of devices is equally important. Advise your employees to never leave their devices unattended in public places and to use strong passwords or biometric security features to lock their devices.
Encrypting the data on devices adds an additional layer of security, making it difficult for unauthorized individuals to access information even if the device is lost or stolen.
Importance of Securing Physical Devices
- Data Protection: Physical devices often contain sensitive information. If a device falls into the wrong hands, it can lead to data breaches, identity theft, and unauthorized access to private or corporate networks.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries are governed by regulations that mandate the protection of sensitive data. Failure to secure physical devices can result in non-compliance, leading to fines and damage to reputation.
- Preventing Unauthorized Access: Securing physical devices helps prevent unauthorized users from gaining access to them, thereby safeguarding the information stored on these devices from malicious use.
Best Practices for Physical Device Security
- Use Strong Access Controls: Implement strong passwords, PIN codes, or biometric authentication (such as fingerprint or facial recognition) to secure devices. This can help prevent unauthorized access if a device is lost or stolen.
- Enable Encryption: Encrypt the storage on devices to protect the data they contain. Encryption ensures that even if a device is compromised, the data it holds is unreadable without the necessary decryption key.
- Physical Locks and Security Cables: For desktop computers and laptops used in public or semi-public places, physical locks and security cables can deter theft.
- Secure Storage: When not in use, devices should be stored in a secure, locked location. This is particularly important for mobile devices and laptops, which are easily portable and, therefore, more susceptible to theft.
- Maintain an Inventory: Keep an up-to-date inventory of all devices, including their make, model, serial number, and assigned user. This can aid in recovery efforts if a device is lost or stolen and helps ensure that all devices are accounted for and properly maintained.
- Implement Remote Wipe Capabilities: For devices that may contain sensitive information, enable remote wipe capabilities. This allows your organization to remotely erase the data on a device if it is lost or stolen, reducing the risk of data breaches.
- Regular Backups: Ensure regular backups of important data from physical devices. In the event of loss, theft, or damage, backups can prevent the permanent loss of critical information.
- Awareness and Training: Educate your employees and users about the importance of physical device security. This includes safe usage practices, the importance of reporting lost or stolen devices immediately, and how to securely store devices when not in use.
#5: Fostering a Culture of Security Awareness
Creating a culture of security awareness within your organization is the most important best practice. Regular training sessions should be conducted to educate employees about the latest cyber threats and the best practices for mitigating these risks.
Encouraging your employees to report suspicious activities and providing them with the tools and knowledge to do so can significantly enhance your organization’s cybersecurity posture.
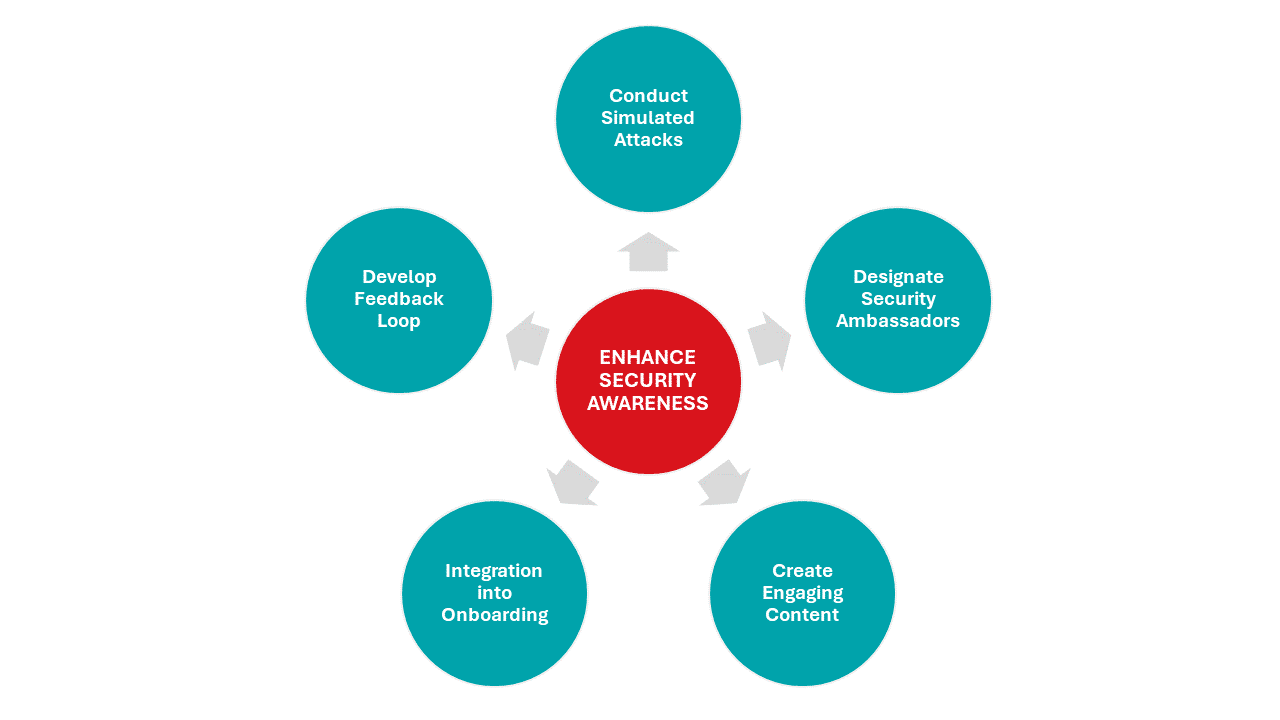
Key Components of a Security Awareness Culture
- Leadership Commitment: Your senior management must demonstrate a commitment to security awareness, setting a precedent for the entire organization. This includes allocating resources for security training and recognizing security as a critical aspect of your organization’s success.
- Continuous Education and Training: Regular training sessions should be conducted to educate your employees about the latest security threats and best practices. Training should be engaging, relevant, and tailored to different roles within your organization, ensuring that all your employees understand their role in maintaining security.
- Effective Communication: Clear and consistent communication about security policies, procedures, and expectations is crucial. This includes regular updates on emerging threats, sharing stories of attempted or successful cyberattacks, and tips on how to stay secure.
- Employee Empowerment: Your employees should be encouraged to take personal responsibility for security. This can be achieved by providing them with the tools and knowledge to recognize threats, report incidents, and contribute to your organization’s security posture.
- Positive Reinforcement: Recognizing and rewarding positive security behaviors can reinforce the importance of security awareness. This could include acknowledging individuals or teams who identify security vulnerabilities, report phishing attempts, or consistently follow security policies.
- Incident Response and Reporting: Establishing clear procedures for reporting and responding to security incidents is critical. Your employees should know how to report a security incident and feel confident that your organization will take appropriate action without assigning blame.
Strategies to Enhance Security Awareness
- Simulated Attacks: Conducting simulated phishing attacks or other security exercises can help employees understand the practical aspects of recognizing and responding to threats. Feedback and training can then be provided based on the outcomes of these simulations.
- Security Ambassadors: Designating security ambassadors within different departments can help spread security awareness throughout your organization. These individuals can serve as points of contact for security questions and help relay information between the security team and their colleagues.
- Engaging Content: Utilizing a variety of formats such as videos, newsletters, and interactive quizzes can make security awareness training more engaging and memorable.
- Integration into Onboarding: Incorporating security awareness into the onboarding process for new employees ensures that they understand your organization’s commitment to security from the start.
- Feedback Loop: Creating a feedback loop where your employees can share their concerns, suggestions, or feedback about security policies and training can help tailor the program to better meet your organization’s needs.

Data Breaches & Emerging Cybersecurity Threats
Data breaches are a critical issue for businesses of all sizes and industries. Data breaches can occur through various means, including cyberattacks, phishing schemes, inadequate security controls, and human error.
When sensitive information such as customer data, financial records, or intellectual property is exposed, it can lead to loss of customer trust, legal penalties, and substantial financial costs associated with remediation efforts, regulatory fines, and potential litigation. Moreover, the aftermath of a breach often requires a substantial investment in enhancing security measures and rebuilding the organization’s reputation.
Organizations and individuals must stay informed about the latest security threats and emerging best practices for security. This includes staying updated on new forms of biometric authentication, advances in encryption technologies, and innovative physical security solutions.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity is a shared responsibility that requires the active participation of all your employees. By maintaining strong passwords, being vigilant against phishing attempts, regularly updating software, securing physical devices, and fostering a culture of security awareness, your employees can play a crucial role in protecting your organization from cyber threats.
About thirtyone3 technology
thirtyone3 technology provides you with the necessary security solutions to avoid breaches while protecting your data and systems from potential threats. This includes regular security updates, malware protection, data backups, endpoint monitoring, and other actions to help keep your business safe from cyberattacks.
Whether you need complete IT support or solutions that complement your existing resources, we are the IT partner that your business needs. Gain peace of mind knowing thirtyone3 technology has you covered.
If you have questions regarding your cybersecurity efforts or would like to schedule a security assessment, contact our tech experts at 623.850.5392 or by email at inquiries@thirtyone3technology.com.

