In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, developing an effective IT strategy is more critical than ever for organizations aiming to stay competitive and foster innovation. An IT strategy serves as the backbone of your technology initiatives, ensuring that they are aligned with business goals and capable of driving growth and operational excellence.
At thirtyone3 technology, we understand that creating a comprehensive IT strategy can be a complex and daunting task. The goal of this article is to provide actionable insights and proven tips to help streamline this process.
From aligning IT with your business objectives to setting clear, measurable goals, involving key stakeholders, and future-proofing your technology plans, we cover the essential elements that contribute to a successful IT strategy.
Our approach demystifies IT strategic planning, transforming your IT department from a traditional support function into a pivotal driver of business success. With the right strategy, your organization can optimize operations, enhance innovation, and gain a significant competitive edge.
Whether you are an IT professional seeking to refine your strategy or a business leader aiming to enhance your organization’s technology framework, this article is designed to help you navigate the complexities and harness the full potential of your IT capabilities.
- 1. What is IT Strategic Planning?
- 2. The Role of IT Strategic Planning in Aligning Technology with Business Goals
- 3. Key Elements of IT Strategic Planning
- 4. Strategies to Ensure IT Supports Overall Business Objectives
- 5. Setting Clear Objectives
- 6. Methods to Track Progress and Measure Success
- 7. Involve Key Stakeholders
- 8. Benefits of Stakeholder Involvement for IT Strategy Success
- 9. Future-Proofing Your IT Strategy
- 10. Create a Roadmap for Continuous Improvement
- 11. IT Strategy Best Practices
- 12. Common Challenges in Developing an IT Strategy
- 13. Strategies to Overcome Challenges
- 14. How an IT Consultant Can Help
- 15. Need Help Getting Started?
- 16. Related Articles
What is IT Strategic Planning?
IT strategic planning is the cornerstone of a successful IT strategy. It involves defining how technology will support the overall business goals and objectives of an organization. Effective IT strategic planning ensures that technology initiatives are not developed in isolation but are integrated into the broader business strategy.
Importance of IT Strategic Planning
IT strategic planning is a systematic process for determining the best way to use technology resources to achieve business goals. This involves assessing current IT capabilities, identifying future technology needs, and aligning IT projects with business objectives. The importance of IT strategic planning lies in its ability to provide a clear direction for IT investments, ensuring that every technology initiative contributes to the organization’s overall success.
A well-crafted IT strategic plan helps organizations avoid common pitfalls such as redundant technology investments, misalignment between IT and business goals, and the inability to adapt to changing market conditions. By establishing a coherent strategy, businesses can better manage their technology resources, improve operational efficiency, and support innovation.
The Role of IT Strategic Planning in Aligning Technology with Business Goals
One of the primary functions of IT strategic planning is to ensure that IT initiatives are aligned with business goals. This alignment is crucial because it ensures that technology investments directly contribute to the achievement of business objectives, such as increasing revenue, improving customer satisfaction, or enhancing operational efficiency.
To achieve alignment, IT strategic planning involves close collaboration between IT leaders and business stakeholders. This collaboration helps ensure that IT understands the business’s strategic direction and can design technology solutions that support it. By aligning IT with business goals, organizations can create synergies that drive overall success.
Key Elements of IT Strategic Planning

Effective IT strategic planning involves several key elements:
- Assessment of Current State: Understanding the existing IT infrastructure, capabilities, and resources is the first step in IT strategic planning. This assessment helps identify strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement.
- Vision and Mission: Defining a clear vision and mission for IT provides direction and purpose. The vision outlines what the organization aims to achieve with its technology, while the mission describes how it will achieve these goals.
- SWOT Analysis: Conducting a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) helps identify internal and external factors that can impact the IT strategy. This analysis provides valuable insights for strategic decision-making.
- Goals and Objectives: Setting clear, measurable goals and objectives is essential for tracking progress and measuring success. These goals should be aligned with the organization’s overall business objectives.
- Roadmap: Developing a detailed roadmap that outlines the steps required to achieve the IT strategy is crucial. The roadmap should include timelines, milestones, and key deliverables to ensure that the strategy is implemented effectively.
- Continuous Improvement: IT strategic planning is not a one-time activity. It requires continuous monitoring and adjustment to respond to changing business needs and technological advancements. Regular reviews and updates to the IT strategy help ensure its ongoing relevance and effectiveness.
Strategies to Ensure IT Supports Overall Business Objectives
To achieve alignment between IT and business goals, organizations can employ several strategies:
- Close Collaboration Between IT and Business Leaders: Regular communication and collaboration between IT and business leaders are essential. This collaboration ensures that IT understands the business’s strategic direction and can develop technology solutions that support it.
- Integrated Planning Processes: Integrating IT strategic planning with overall business planning helps ensure that technology initiatives are considered in the context of broader business goals. This integration can be achieved through joint planning sessions, shared strategic objectives, and cross-functional teams.
- Business-Driven IT Projects: Prioritizing IT projects based on their alignment with business objectives helps ensure that technology investments deliver maximum value. This prioritization can be achieved by evaluating potential IT initiatives based on their expected business impact, return on investment (ROI), and strategic importance.
- Performance Metrics: Establishing performance metrics that link IT performance to business outcomes helps ensure alignment. These metrics can include key performance indicators (KPIs) such as cost savings, revenue growth, customer satisfaction, and operational efficiency. Regularly tracking and reporting these metrics helps ensure that IT initiatives remain aligned with business goals.
Examples of Successful IT and Business Alignment
Example #1: Retail Industry
A leading retail chain successfully aligned its IT strategy with its business goals by implementing an integrated e-commerce platform. This platform enabled seamless online and offline shopping experiences, driving sales growth, and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Example #2: Healthcare Sector
A healthcare provider aligned its IT strategy with its business objectives by deploying an advanced electronic health records (EHR) system. This system improved patient care, streamlined operations, and supported the organization’s goal of becoming a leader in patient-centered care.
Example #3: Financial Services
A financial services firm aligned its IT initiatives with its strategic goal of enhancing customer experience by implementing a robust data analytics platform. This platform provided valuable insights into customer behavior, enabling personalized services and improved customer retention.
Setting Clear Objectives
Setting clear and measurable objectives is a crucial step in developing an effective IT strategy. Objectives provide a roadmap for IT initiatives, ensuring that every project and investment supports the organization’s overarching goals. Clear objectives help track progress, measure success, and make informed decisions throughout the strategic planning process.
Importance of Clear and Measurable Objectives
- Guidance and Focus: Clear objectives offer guidance and focus for the IT team, helping them understand what needs to be achieved and why. This focus ensures that efforts are directed toward activities that have the most significant impact on the organization.
- Performance Measurement: Measurable objectives allow organizations to track progress and evaluate the effectiveness of their IT strategy. This measurement is essential for identifying areas of success and opportunities for improvement.
- Resource Allocation: Setting clear objectives helps prioritize IT initiatives and allocate resources effectively. By understanding which projects align most closely with business goals, organizations can make informed decisions about where to invest time, money, and personnel.
- Accountability: Defined objectives create accountability within the IT team. When objectives are clear, team members understand their responsibilities and can be held accountable for their contributions to the strategy’s success.
Steps to Define and Set IT Objectives
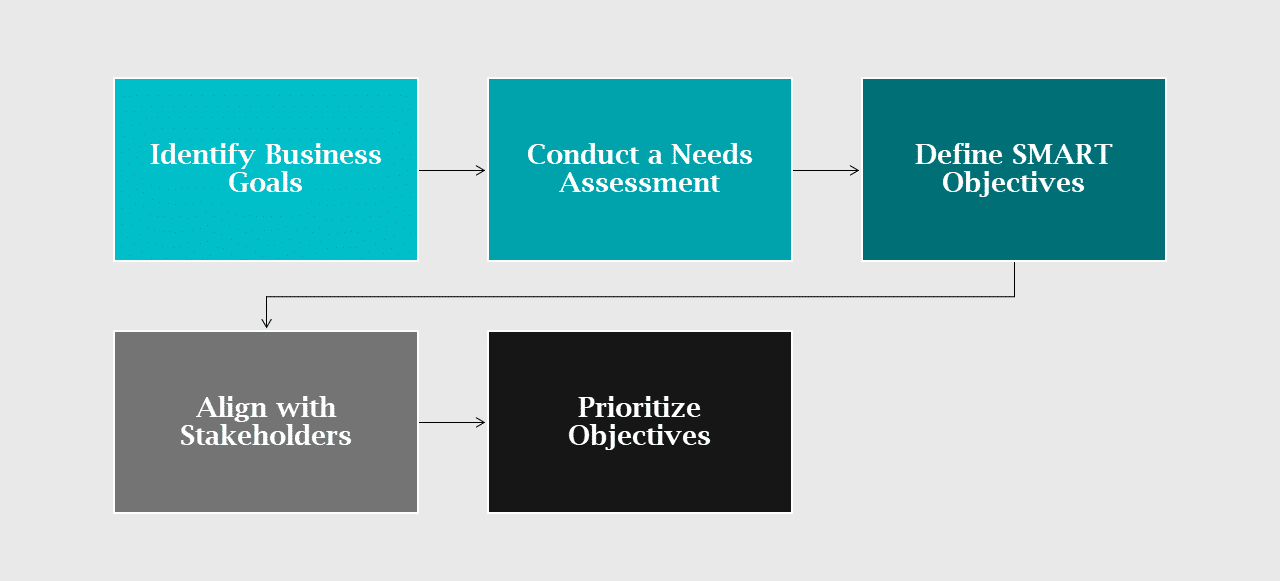
- Identify Business Goals: Start by understanding the organization’s business goals. These goals provide the foundation for IT objectives, ensuring that technology initiatives support the broader business strategy.
- Conduct a Needs Assessment: Assess the current state of IT within the organization, identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This assessment helps pinpoint areas where IT can have the most significant impact.
- Define SMART Objectives: Set objectives that are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART). SMART objectives provide clear criteria for success, making it easier to track progress and measure outcomes.
- Align with Stakeholders: Engage key stakeholders in the objective-setting process. This alignment ensures that objectives are relevant to the business and have the support needed for successful implementation.
- Prioritize Objectives: Not all objectives will have the same level of importance. Prioritize objectives based on their potential impact on business goals, resource requirements, and feasibility.
Methods to Track Progress and Measure Success
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Establish KPIs that are linked to IT objectives. KPIs provide quantifiable measures of success, such as system uptime, project completion rates, user satisfaction, and cost savings.
Regular Reporting: Implement a reporting system to track progress against objectives. Regular reports provide visibility into the status of IT initiatives and highlight any areas that require attention.
Performance Reviews: Conduct periodic performance reviews to assess progress toward objectives. These reviews offer an opportunity to celebrate successes, address challenges, and make necessary adjustments to the strategy.
Feedback Loops: Create feedback loops that allow for continuous improvement. Solicit feedback from stakeholders, end-users, and IT team members to gain insights into what is working well and where improvements are needed.
Benchmarking: Compare performance against industry benchmarks and best practices. Benchmarking provides a context for evaluating success and identifying areas for improvement.

Involve Key Stakeholders
Involving key stakeholders in the IT strategic planning process is essential for the success of any IT strategy. Stakeholders bring diverse perspectives, insights, and expertise that can enhance the strategy’s relevance and effectiveness. Their involvement ensures that the IT strategy is aligned with business needs and has the necessary support for successful implementation.
Identifying Key Stakeholders in IT Strategic Planning
Executive Leadership: Executives, including the CEO, CFO, and other C-suite members, play a crucial role in IT strategic planning. Their vision and strategic direction shape the overall business goals that the IT strategy must support.
IT Leadership: The Chief Information Officer (CIO) and IT directors provide essential technical expertise and ensure that the strategy aligns with current and future technological capabilities.
Business Unit Leaders: Leaders of various business units, such as marketing, sales, operations, and finance, offer insights into how IT can support their specific needs and objectives. Their involvement helps ensure that the IT strategy addresses the diverse requirements of different departments.
End-Users: Employees who use IT systems and applications daily can provide valuable feedback on current challenges and potential improvements. Involving end-users helps create a strategy that enhances user experience and adoption.
External Partners: Vendors, consultants, and other external partners can offer industry best practices, innovative solutions, and an outside perspective. Their input can be valuable in shaping a forward-thinking IT strategy.
Strategies to Involve Stakeholders in the Process
- Stakeholder Workshops: Conduct workshops and brainstorming sessions to gather input from stakeholders. These sessions facilitate open communication and collaborative problem-solving, ensuring that diverse perspectives are considered.
- Regular Communication: Maintain regular communication with stakeholders throughout the strategic planning process. Use meetings, progress reports, and updates to keep stakeholders informed and engaged.
- Collaborative Planning: Involve stakeholders in collaborative planning activities, such as developing the vision and mission, conducting SWOT analyses, and setting objectives. This collaboration ensures that the strategy reflects the collective input of all relevant parties.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Establish mechanisms for stakeholders to provide ongoing feedback, such as surveys, focus groups, and suggestion boxes. This feedback helps identify emerging issues and opportunities for improvement.
- Governance Structures: Create governance structures, such as steering committees or advisory boards, to oversee the IT strategic planning process. These structures ensure that stakeholders have a formal role in decision-making and accountability.
Benefits of Stakeholder Involvement for IT Strategy Success
Enhanced Relevance: Stakeholder involvement ensures that the IT strategy is relevant to the needs of the business. By incorporating diverse perspectives, the strategy is more likely to address critical challenges and opportunities.
Increased Buy-In: When stakeholders are involved in the planning process, they are more likely to support the strategy and champion its implementation. This buy-in is crucial for overcoming resistance to change and ensuring successful execution.
Improved Decision-Making: Stakeholders bring valuable knowledge and expertise to the table, enhancing the quality of decision-making. Their input helps identify potential risks, benefits, and trade-offs, leading to more informed strategic choices.
Stronger Collaboration: Involving stakeholders fosters a culture of collaboration and teamwork. This collaboration strengthens relationships between IT and business units, promoting a unified approach to achieving organizational goals.
Greater Flexibility: Stakeholder input helps create a flexible and adaptive IT strategy. By considering diverse perspectives and anticipating potential challenges, the strategy is better equipped to respond to changing business needs and technological advancements.

Future-Proofing Your IT Strategy
Future-proofing your IT strategy is essential to ensure that your organization can adapt to technological advancements and evolving business needs. By focusing on flexibility, scalability, and resilience, you can create an IT strategy that remains relevant and effective in the face of change.
Flexibility and Scalability in an IT Strategy
Adaptability to Change: A flexible IT strategy allows your organization to respond swiftly to market changes, emerging technologies, and evolving business priorities. This adaptability is crucial in a dynamic business environment where change is constant.
Growth and Expansion: Scalability ensures that your IT infrastructure can grow with your business. As your organization expands, your IT systems must be able to handle increased workloads, additional users, and more complex processes without compromising performance.
Cost Efficiency: Flexible and scalable IT solutions can help manage costs more effectively. By scaling resources up or down based on demand, you can optimize IT spending and avoid unnecessary expenses.
Incorporating Emerging Technologies and Trends
Stay Informed: Regularly monitor industry trends and emerging technologies. Subscribe to industry publications, attend conferences, and participate in professional networks to stay informed about the latest developments.
Evaluate and Experiment: Assess the potential impact of modern technologies on your business. Conduct pilot projects and proof-of-concept tests to evaluate their feasibility and benefits before full-scale implementation.
Adopt a Phased Approach: Implement innovative technologies in phases to minimize disruption and manage risks. A phased approach allows you to learn from initial deployments and make necessary adjustments before scaling up.
Invest in Training: Ensure that your IT staff and end-users are trained in newly implemented technologies. Ongoing training and development help maximize the benefits of new tools and systems, ensuring smooth adoption and effective use.
Ensuring Cybersecurity Measures
Comprehensive Security Strategy: Develop a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy that includes policies, procedures, and technologies to protect your IT assets. This strategy should cover data protection, network security, endpoint security, and incident response.
Regular Risk Assessments: Conduct regular risk assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities and threats. These assessments help prioritize security investments and ensure that your defenses remain robust against evolving threats.
Implement Multi-Layered Security: Use a multi-layered security approach to provide multiple lines of defense. This approach includes firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption, and access controls to protect against a wide range of threats.
Continuous Monitoring: Implement continuous monitoring to detect and respond to security incidents in real-time. Monitoring helps identify unusual activity and potential breaches, allowing for swift action to mitigate risks.
Create a Roadmap for Continuous Improvement
- Set Long-Term Goals: Define long-term goals for your IT strategy that align with your business vision and objectives. These goals provide a clear direction for future IT initiatives and investments.
- Develop a Detailed Roadmap: Create a roadmap that outlines the steps required to achieve your long-term goals. The roadmap should include timelines, milestones, and key deliverables to ensure that progress is tracked and measured.
- Regular Reviews and Updates: Schedule regular reviews of your IT strategy and roadmap to ensure they remain relevant and effective. Updates should be made based on changes in business priorities, technological advancements, and feedback from stakeholders.
- Foster a Culture of Innovation: Encourage a culture of innovation within your IT team and across the organization. This culture supports continuous improvement by promoting creativity, experimentation, and the adoption of current ideas and technologies.
- Measure and Report Progress: Establish metrics to measure the success of your IT strategy and report progress to stakeholders. Regular reporting ensures transparency and accountability, helping to maintain support and momentum for ongoing initiatives.
IT Strategy Best Practices
Involve Key Stakeholders
Collaborative Planning: Engage stakeholders from various departments, including executive leadership, IT teams, and business unit leaders, in the planning process. Their input ensures the strategy addresses diverse needs and perspectives.
Regular Communication: Maintain open and regular communication with stakeholders throughout the strategy’s development and implementation phases. This helps build consensus, address concerns, and ensure ongoing support.
Focus on Flexibility and Scalability
Modular Architecture: Design IT systems with modular architecture to enable flexibility and scalability. This approach allows for easier updates, integration of new technologies, and scaling of resources based on demand.
Cloud Solutions: Leverage cloud computing solutions for scalable and flexible IT infrastructure. Cloud services offer on-demand resources, reducing the need for significant upfront investments and allowing for rapid scaling.
Incorporate Cybersecurity Measures
Proactive Security Posture: Adopt a proactive approach to cybersecurity by implementing robust security measures, conducting regular risk assessments, and staying updated on the latest threats and vulnerabilities.
Security by Design: Integrate security into the design and development of IT systems and applications. This approach ensures that security is a foundational aspect rather than an afterthought.
Emphasize User Experience and Adoption
User-Centric Design: Prioritize user experience in the design and implementation of IT solutions. User-friendly interfaces and intuitive workflows enhance adoption and satisfaction.
Training and Support: Provide comprehensive training and ongoing support to users to facilitate smooth adoption of modern technologies. Effective training programs help users understand the benefits and functionalities of IT solutions.
Regularly Reviewing and Updating the Strategy
Continuous Improvement: Establish a process for continuous improvement, regularly reviewing and updating the IT strategy to reflect changing business needs, technological advancements, and feedback from stakeholders.
Performance Metrics: Use performance metrics to track the success of the IT strategy. Regularly measure and report on key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess progress and make informed adjustments.

Common Challenges in Developing an IT Strategy
Lack of Alignment Between IT and Business Goals
Miscommunication: One of the most significant challenges is the misalignment between IT initiatives and business objectives. This often arises from poor communication between IT and business leaders, leading to technology investments that do not support strategic goals.
Siloed Operations: When IT operates in isolation from other business units, it can result in a disconnect between technological capabilities and business needs. This siloed approach hinders collaboration and integration, reducing the overall effectiveness of the IT strategy.
Resource Constraints
Budget Limitations: Limited financial resources can constrain the ability to invest in necessary IT infrastructure, tools, and personnel. Budget constraints often force organizations to prioritize certain initiatives over others, which can delay or derail strategic goals.
Talent Shortages: The demand for skilled IT professionals often exceeds the supply, leading to talent shortages. This scarcity of qualified personnel can impede the development and implementation of an effective IT strategy.
Time Constraints: Developing a comprehensive IT strategy requires considerable time and effort. Competing priorities and day-to-day operational demands can limit the time available for strategic planning.
Rapid Technological Changes
Keeping Up with Innovation: The fast pace of technological innovation presents a challenge for organizations striving to keep their IT strategies current. Modern technologies and trends emerge regularly, requiring continuous monitoring and adaptation.
Legacy Systems: Many organizations struggle with outdated legacy systems that are difficult to integrate with innovative technologies. These systems can hinder modernization efforts and limit the flexibility of the IT strategy.
Resistance to Change
Cultural Barriers: Organizational culture can be a significant barrier to change. Resistance from employees who are accustomed to existing processes and systems can slow down the adoption of new technologies and hinder the execution of the IT strategy.
Change Management: Effective change management is essential for successful IT strategy implementation. Without proper planning and communication, even well-designed strategies can face resistance and fail to achieve their objectives.

Strategies to Overcome Challenges
- Enhance Communication and Collaboration: Foster open communication and collaboration between IT and business leaders. Regular meetings, joint planning sessions, and integrated teams can help align IT initiatives with business goals.
- Prioritize and Allocate Resources: Develop a clear prioritization framework for IT initiatives based on their alignment with strategic goals. Allocate resources efficiently, considering budget, talent, and time constraints.
- Invest in Continuous Learning: Encourage continuous learning and professional development for IT staff to keep up with technological advancements. Provide training opportunities and support for certifications to address talent shortages.
- Adopt a Phased Approach: Implement innovative technologies and strategic initiatives in phases. This approach allows for gradual adoption, reduces risk, and provides opportunities for feedback and adjustments.
- Develop a Change Management Plan: Create a comprehensive change management plan that includes communication strategies, training programs, and support systems. Engage employees early in the process to build buy-in and reduce resistance.
How an IT Consultant Can Help
Hiring an IT consultant can be a momentous change for organizations looking to develop and implement an effective IT strategy. IT consultants bring a wealth of expertise, experience, and an objective perspective that can significantly enhance the strategic planning process and ensure successful execution.
The Role of an IT Consultant in IT Strategic Planning
Expert Analysis: IT consultants provide expert analysis of an organization’s current IT infrastructure, capabilities, and needs. Their comprehensive assessments help identify gaps, inefficiencies, and opportunities for improvement.
Strategic Alignment: Consultants ensure that IT initiatives are closely aligned with business goals. They facilitate collaboration between IT and business leaders, helping to create a unified vision and strategy.
Technology Roadmap: IT consultants assist in developing a detailed technology roadmap that outlines the steps needed to achieve strategic objectives. This roadmap includes timelines, milestones, and key deliverables, ensuring a clear path forward.
Risk Management: Experienced consultants identify potential risks and develop mitigation strategies to minimize disruptions. Their expertise in risk management helps ensure that the IT strategy is robust and resilient.
Change Management: IT consultants support change management efforts by developing comprehensive plans that include communication strategies, training programs, and stakeholder engagement. This support helps facilitate smooth transitions and high adoption rates for innovative technologies.
Benefits of Hiring an IT Consultant
Expertise and Experience: IT consultants bring specialized knowledge and extensive experience from working with various industries and organizations. Their expertise helps ensure that the IT strategy is based on best practices and innovative solutions.
Objectivity: As external parties, consultants offer an objective perspective, free from internal biases and politics. Their unbiased insights can help identify issues that may be overlooked by internal teams.
Efficiency: Consultants can expedite the strategic planning process by applying their proven methodologies and frameworks. This efficiency allows organizations to develop and implement their IT strategies more quickly and effectively.
Cost Savings: While hiring an IT consultant involves an upfront investment, their expertise can lead to significant cost savings overall. By optimizing IT resources, improving efficiency, and avoiding costly mistakes, consultants can deliver substantial ROI.
Access to Best Practices: IT consultants stay up to date with the latest industry trends, technologies, and best practices. Their knowledge ensures that the IT strategy incorporates innovative solutions that drive competitive advantage.
About thirtyone3 technology
Organizations face mounting challenges in aligning their technology initiatives with business goals, optimizing operations, and staying ahead of the competition. The tension is palpable, and the stakes are high: without a robust IT strategy, your organization risks falling behind, wasting resources, and missing opportunities for growth and innovation.
But here is the relief: thirtyone3 technology is here to guide you through this complex journey. With extensive experience and deep expertise, we simplify the process of IT strategic planning, transforming it from a daunting task into a manageable and rewarding endeavor.
We understand the critical elements that make an IT strategy successful. By aligning IT with your business objectives, setting clear and measurable goals, involving key stakeholders, and future-proofing your technology plans, we ensure that your IT initiatives are not just functional, but transformative. Our approach demystifies IT strategic planning, turning your IT department into a pivotal driver of business success rather than a mere support function.
At thirtyone3 technology, we pride ourselves on our tailored solutions and proven methodologies. Our seasoned consultants bring a wealth of knowledge and best practices, ensuring your IT strategy is not only aligned with your business goals but also adaptable to future changes. We provide the expertise needed to optimize operations, enhance innovation, and gain a significant competitive edge.
So, whether you are an IT professional seeking to refine your strategy or a business leader aiming to bolster your organization’s technology framework, thirtyone3 technology offers the insights and support you need. Let us help you navigate the complexities and harness the full potential of your IT capabilities, positioning your organization for sustained success in a rapidly evolving digital world.

